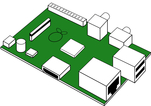
 In my eighth lesson, I decided to give my students a test to see what they had learnt so far. I followed this with an introduction to the Raspberry Pi. Learning Objectives:
Lesson 1: Theory Test Suggested time: 50 mins Test: I used the Hardware theory test (OCR Unit 2.1.2) courtesy of Mark Clarkson. You can download the test for FREE here: OCR GCSE Computing Hardware Unit Test Plenary: I asked students to swap papers and went through the answers. I also explained to students the model answers using the marking criteria (Click here) Lesson 2: Introduction to the Raspberry Pi Suggested time: 50 mins Starter: I split the class into groups of 4. I then gave each group a boxed Raspberry Pi and worksheet (See below).
After handing out the worksheets, I asked the students to un-box their Raspberry Pis and try to identify each of the different parts of the device using their worksheet. (This is also a great opportunity to recap some of the Hardware theory elements such as CPU, Input / Output, memory and storage etc.). Alternatively: You could also use the Interactive Flash based Drag-and-drop version which can be found on the OCR website: http://www.ocr.org.uk/Images/127399-raspberry-pi-drag-drop-activity.swf Once all the students had filled in their worksheets, I reviewed their answers. What is a Raspberry Pi? The Raspberry Pi is a low cost, credit-card sized, programmable computer which has been developed by the Raspberry Pi Foundation. How can I get hold of one? You can buy the Raspberry Pi through a variety of online retailers such as Amazon, RS Components, CPC, maplin etc. How much does one cost? The Model A will typically cost £20 and the Model B £30. Note: this does not include the SD Card, keyboard, mouse and monitor required to use the Pi. It is assumed that most of these components will already available in school. SD cards can be picked up relatively cheaply online. To find out more about the Raspberry Pi, visit the official website. Note: As part of their drive to encourage the teaching of computing, OCR are offering free Raspberry Pis to schools who wish to increase the engagement of Computing and IT. To express your interest in receiving FREE Raspberry Pis for your school, visit the following link and complete the attached form: http://www.ocr.org.uk/qualifications/by-subject/computing/free-raspberry-pi/ Main:
I divided the class into pairs and gave each pair a Raspberry Pi, SD Memory Card and set of instructions for setting up the Raspberry Pi. I then instructed the students to connect and setup their Pis. Note: The Raspberry Pi do not come with a pre-installed Operating System therefore, the students will have to install the OS themselves. This is a good opportunity to introduce the software theory element of the course and explain the importance of the Operating System. You can download a disk image of the operating system from the official Raspberry Pi website www.raspberrypi.org/downloads (The recommended operating system is Raspbian “wheezy”). In order to write the disk image (.img) file to the SD card you will need a program called Win32 Disk Imager. Download Here. Due to network restrictions and as Win32 Disk Imager, if used incorrectly, can harm your machine, for the purpose of this task, I provided the students with an old laptop with the Disk Imager software already installed and a copy of the latest Raspberry Pi OS in (.img) format on a USB pen. Extension Task: Students attempted the OCR “Raspberry Pi Architecture Classroom Challenge” http://www.ocr.org.uk/Images/125296-classroom-challenge-architecture-learner-sheet.pdf Model answers for the challenge can be found here: http://www.ocr.org.uk/Images/125297-classroom-challenge-architecture-teacher-sheet.pdf Comments are closed.
|
AuthorSimon Johnson Microsoft Innovative Educator Expert / MIE Trainer
Minecraft Cert. Educator / Global Mentor
CAS Master Teacher
Raspberry Pi Cert. Educator
Tickle Ambassador
Archives
June 2017
CategoriesAll Algorithms Cpu Fundamentals Hardware Input & Output Memory OCR A451 Software Storage |
||||||
Search by typing & pressing enter






 RSS Feed
RSS Feed
